What are CO₂ certifications?
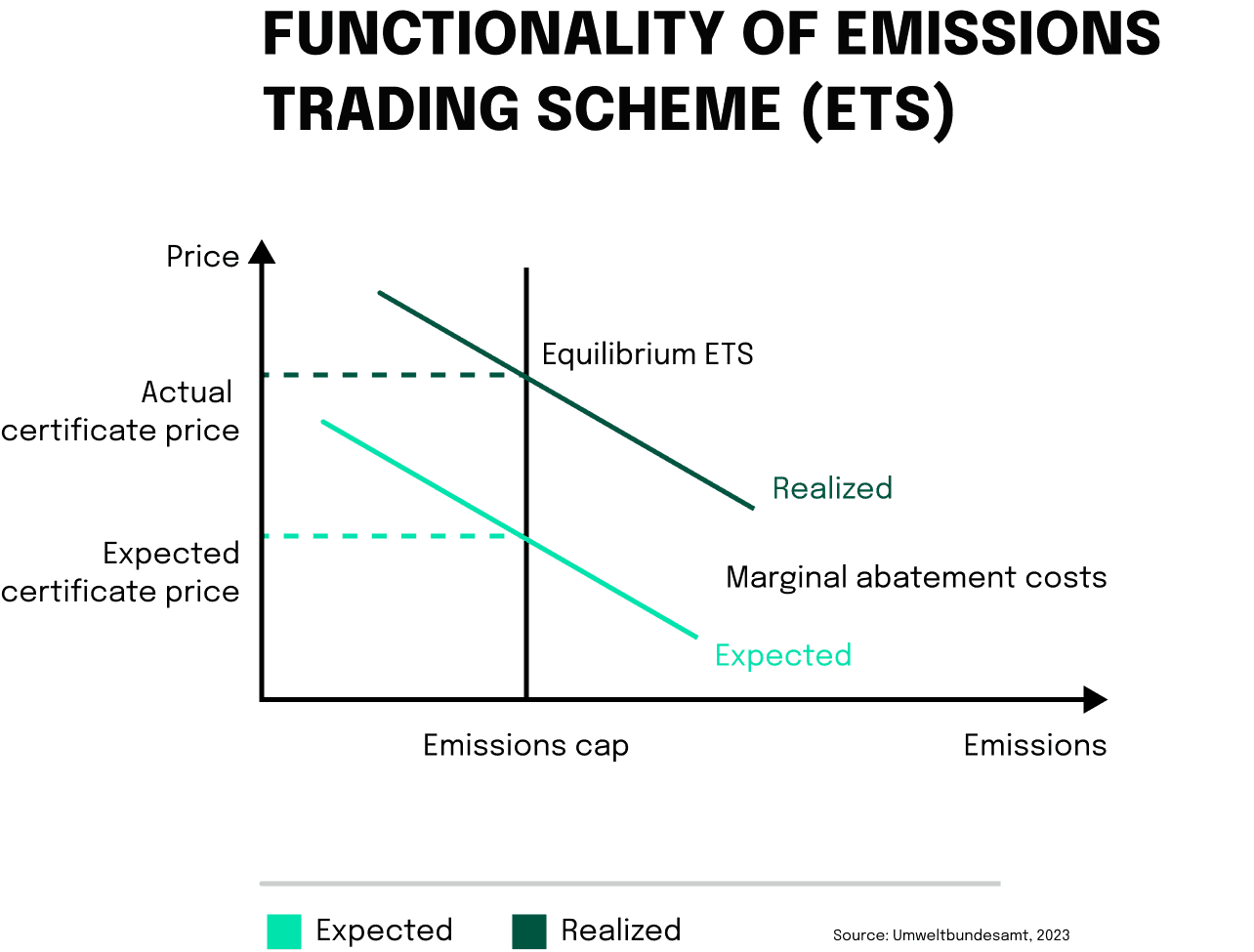
As the ETS is clearly flawed – more downfalls are visible here – there are alternatives that gained in popularity in the last years. Thousands of companies around the world have been able to announce both large and small climate success stories thanks to CO₂ certificates. The Walt Disney Company, for example, has claimed triumphantly that it has slashed its emissions by half since 2012. Gucci has announced that its operations are completely climate neutral. As have McKinsey, Netflix, and Zalando. But how does this actually work, and what are the benefits of these certifications?
CO₂ certificates, also known as carbon offset certificates, are tools designed to signify the decrease or elimination of a certain quantity of greenhouse gas emissions, typically measured in metric tons of CO₂ equivalent. When organizations, projects, or products achieve verified reductions or eliminations of their carbon emissions, these certificates are granted. Businesses can use these certificates to display their dedication to minimizing their carbon impact and combating climate change.
Does this sound too good to be true? The answer is not so straightforward. There are good arguments for the usage of CO₂ certifications, nonetheless, we do not want to neglect the potential downsides and associated reputational risk when relying on the wrong certifications. That’s exactly why we analyzed the risk factors and present them in the fourth section of the article. Keeping these factors in mind, while being guided by the EU Carbon Removal Certification Framework (CRCF) will help you in making the right decision when it comes to the selection of CO certifications.
How are CO₂ certifications created and regulated?
Certification of carbon dioxide removals involves verifying that a certain amount of carbon dioxide has been removed from the atmosphere and stored in a way that is permanent and measurable. This process typically involves third-party verification and certification schemes to ensure that the removals are real, additional, and permanent. Let’s examine this process one step at a time:
- Formulating standards and protocols: Certification bodies like the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) or the Gold Standard create guidelines and methods for measuring, documenting, and verifying reductions or removals of greenhouse gas emissions.
- Project execution: Organizations, businesses, and even governments undertake projects aimed at reducing or removing carbon emissions, such as setting up renewable energy facilities, initiating reforestation efforts, or capturing methane.
- Verification and certification: Independent third-party evaluators examine projects to confirm their compliance with the appropriate standards and protocols. These evaluators authenticate the claims of carbon emissions reduction or removal made by those implementing the projects.
- Regulation and supervision: Governments and international organizations, like the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the European Union, establish a legal and regulatory framework for CO₂ certificates. They create guidelines, set up registries for monitoring certificates, and enforce regulations.
EU Carbon Removal Certification Framework (CRCF)
As we have just mentioned before, the process of creating credible carbon removal certifications is also heavily dependent on regulatory bodies. Now that you have a solid understanding of CO2 certifications let’s delve deeper into the EU Carbon Removal Certification Framework (CRCF). The CRCF, established by the European Commission, is a comprehensive system designed to provide transparent, robust, and science-based certification for carbon removal solutions within the European Union.
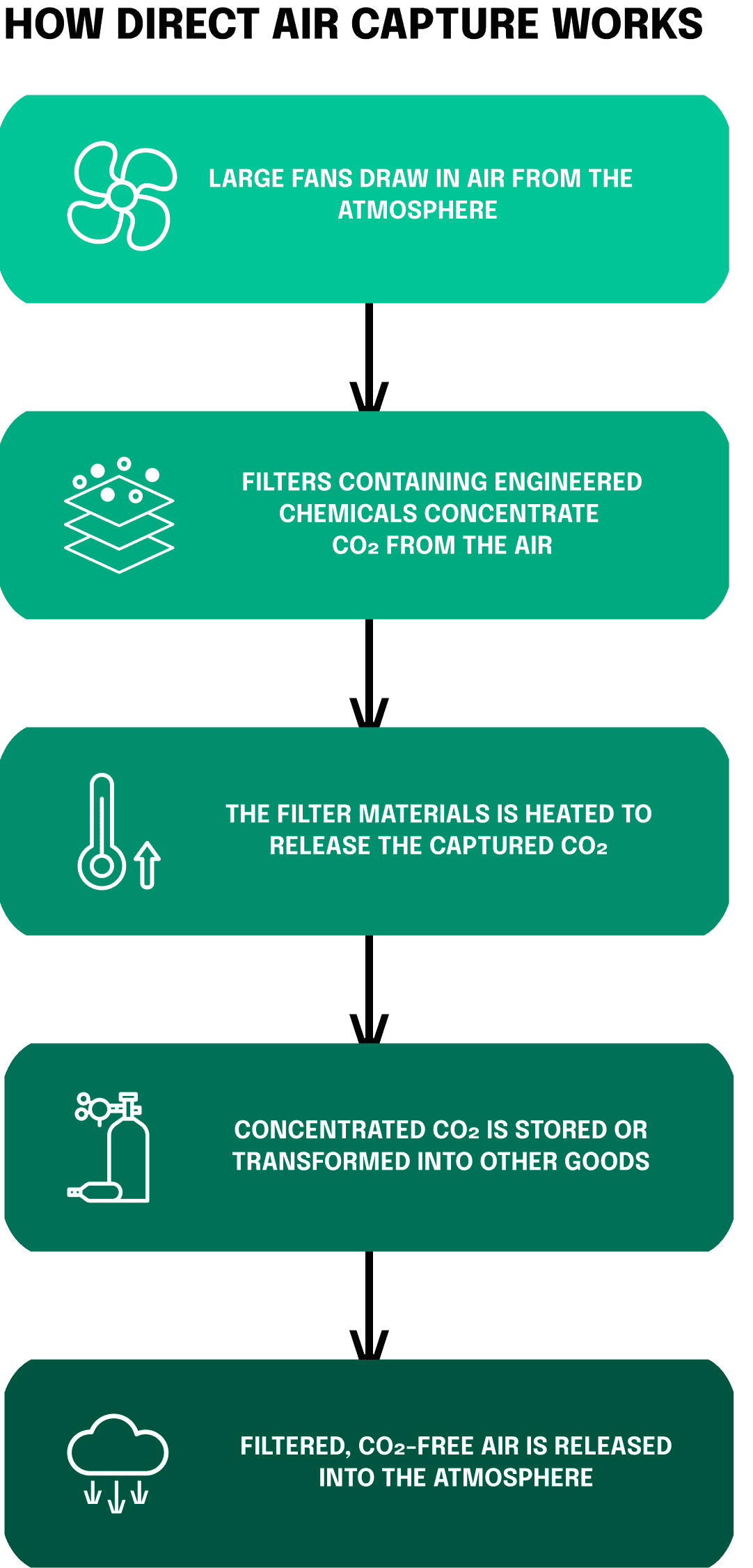
The primary objectives of the CRCF are to encourage investment in carbon removal projects, promote innovative carbon removal technologies, and support the European Union’s goal of achieving climate neutrality by 2050. The framework covers a wide range of carbon removal methods, including afforestation, reforestation, soil carbon sequestration, bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS), enhanced weathering, and direct air capture with storage. In the later stages of this article, we will take a closer look at the different carbon removal methods that are currently being used. Let’s shortly focus on the proposed regulation itself.What exactly are the steps proposed by the EU?
- Application submission: The operator of the carbon removal activity sends an application for certification to a certification body. This application should contain all pertinent information about the carbon removal activity.
- In-depth activity description and methodology used: The operator supplies a comprehensive description of the carbon removal activity and the certification methodology employed. This includes details on how carbon removals will be measured, monitored, and verified.
- Anticipated carbon removals and net carbon removal advantage: The operator records the expected carbon removals and the net carbon removal benefit. This data helps determine if the proposed activity fulfills the minimum requirements for EU-certified carbon removals.
- Certification audit: Assisted by the operator or a group of operators, the certification body performs a certification audit in the initial phase to verify the provided information and ensure compliance with the regulation’s quality criteria.
- Consultation services for smaller operators: If a group of operators submits the application, it should specify how consultation services are offered, particularly to small-scale carbon farming operators. This guarantees that all operators receive the necessary support.
- Certification decision: After reviewing the audit results, the certification body decides whether to grant a certificate for EU-certified carbon removals. If approved, this certificate verifies that all relevant requirements have been met.
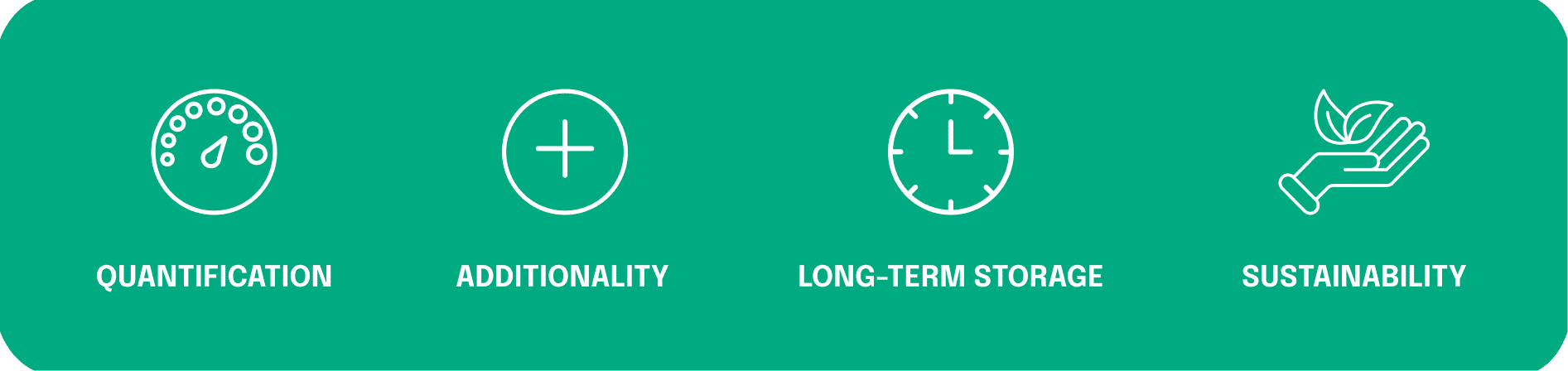
The proposal also sets out requirements for third-party verification and certification of carbon removals, in order to harmonize the certification process and ensure environmental integrity. With the ultimate goal of creating high-quality certification with the following characteristics visible in the graphic below.