Vibe Coding dramatically speeds up software development with AI – an advantage that sounds especially tempting for innovative banks. But the fast track to a prototype comes with its downsides: inconsistent code architecture, missing security standards, and code that hardly works in a team environment. For productive use in sensitive banking operations, Vibe Coding is therefore not well-suited. Used properly in a bank’s innovation work, however, it can be a valuable tool for rapid prototyping, idea validation, and creative problem-solving. 
Vibe Coding’s role in banking: Perfect for testing, risky for production
What Is Vibe Coding and why Is everyone talking about it?
Vibe Coding means creating code with AI from natural language – whether written or spoken. Instead of programming every line manually, users write or say their requirements, and the AI generates executable code. In practice, this “vibed” code is not yet perfect, but it opens up new possibilities. Unlike traditional programming, where developers write all the code themselves, or low-code/no-code platforms that rely on predefined building blocks, Vibe Coding produces real source code. It sits somewhere between hand coding and a drag‑and‑drop toolbox – fast, flexible, and with real output. For banks, this is especially exciting: ideas can be turned directly into clickable prototypes.
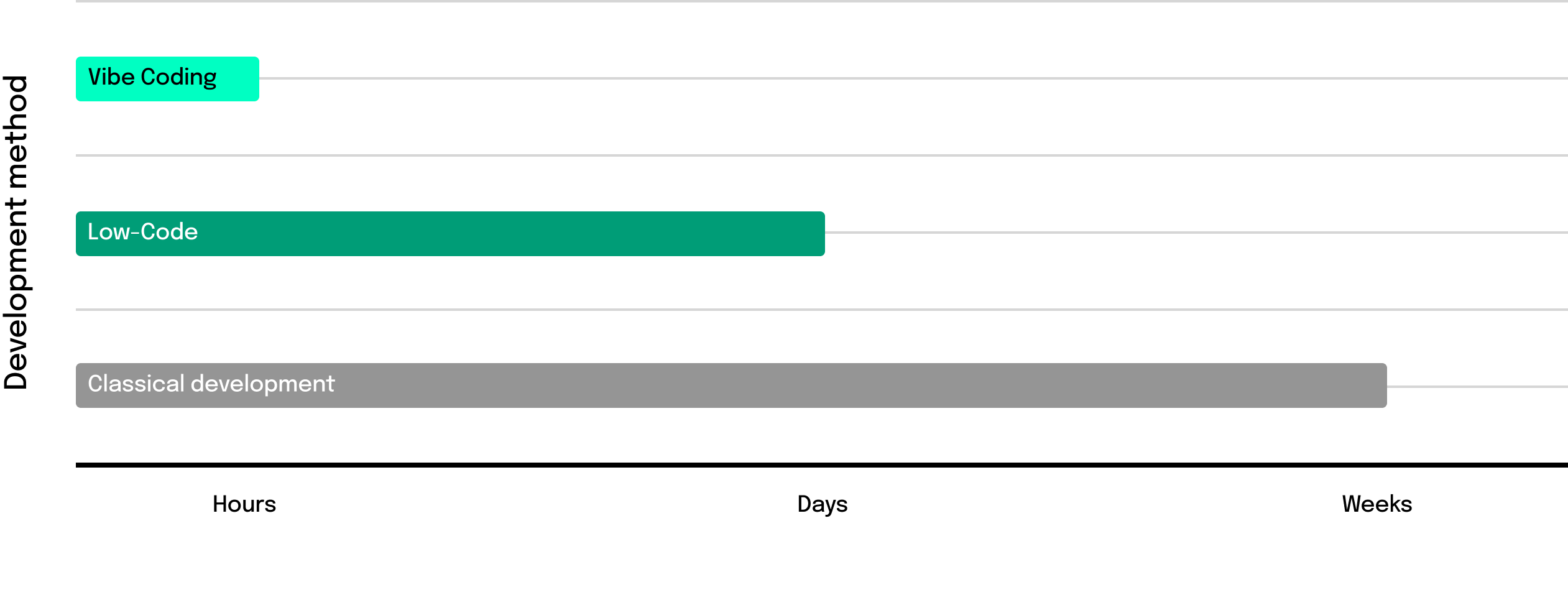
Speed as a prototyping advantage
The biggest plus is speed. With language-based code generation, iterations can be created in hours instead of weeks. Business units can try out ideas right away – even without deep technical know-how. This way, prototypes emerge that can be used for user feedback, internal discussions, or as proof-of-concept. Especially in early innovation phases, that’s a real advantage.
The downside: Inconsistent architecture
But speed has its price. Vibe-generated code rarely follows a clean, scalable architecture. Standards are often missing. Instead of clear structures, complex dependencies emerge that are hard for developers to follow. In addition, the code isn’t written by humans and has to be understood before any changes can be made – and such changes are crucial in live environments.
Live environments are production systems where real customer data and money are processed and that must run stably, securely, and error-free around the clock. This is exactly where Vibe Coding shows its weakness: in collaboration between human and machine, the code is hardly team-ready. In short: it works for prototypes, but is unsuitable for long-term use.
Security and compliance risks in banking
In banking, these weaknesses are particularly serious. It’s not only about sensitive data but also about real money. Banks want to minimize risks – reinforced by strict regulatory requirements that spell out in detail how security and compliance must be implemented. For developers, AI-generated code is often a black box, and the sheer volume of lines of code doesn’t make it more transparent. Without thorough checks, using it in production would be negligent. The problem: testing procedures for AI code are not yet mature. If checks are too superficial, weaknesses remain hidden. If they are too strict, the extra effort cancels out Vibe Coding’s speed advantage.
Why Vibe Coding doesn’t belong in production banking systems
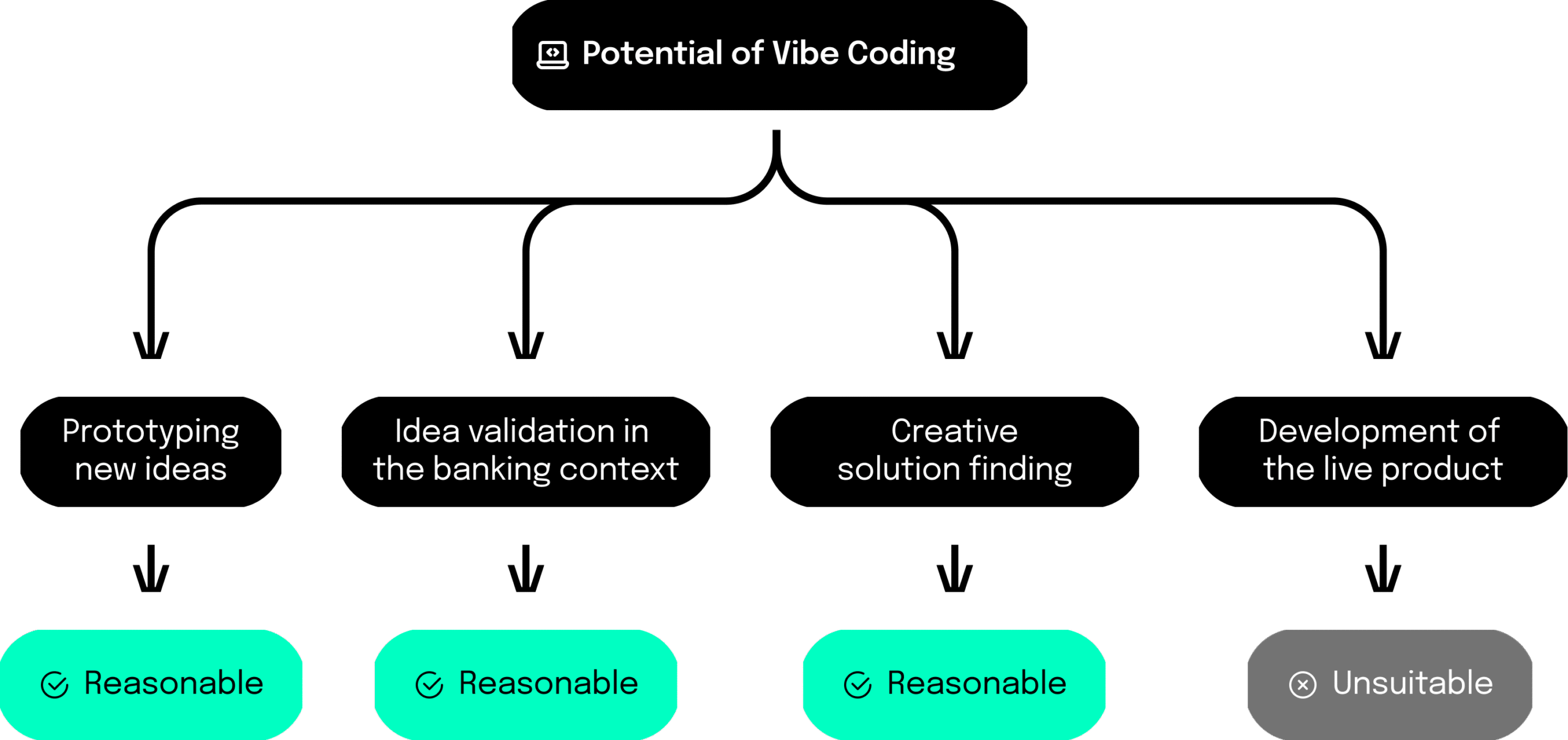
For live systems, banks need verified, maintainable, and secure software. Maintainable means: designed so it can be understood, adapted, and extended in the long term – with clear structure, documentation, and standards. But Vibe Coding generally doesn’t provide that. As a result, the initial speed advantage quickly flips: rework costs time and resources. In critical areas such as payments, compliance, or risk management, Vibe Coding is therefore off-limits. Here, stability and security are non‑negotiable.
Where Vibe Coding makes sense
That doesn’t mean Vibe Coding has no role in banking. On the contrary: when used correctly, it can add real value in innovation work. Suitable use cases include:
- Prototyping new ideas: quick proof-of-concept
- Validating ideas in the banking context: testing concepts before further development
- Creative problem-solving: exploring alternative approaches
Vibe Coding is also useful outside of innovation projects. For example, to practice working with the technology and improve collaboration between developers and non-technical teams. It’s also a smart tool for developers to learn and practice new programming languages. Automatically generated examples provide direct, hands-on understanding.
Best practices for banks
To ensure Vibe Coding stays an advantage rather than a risk, banks should define clear guidelines. Key measures include strict separation of prototype and production code, and clearly defined processes for transitioning prototypes into production-ready code.
Prototypes that prove promising and are intended to go live require solid preparation. That includes:
- Basic documentation: Even AI-generated code needs clear documentation to enable teamwork.
- Automated testing: Unit, integration, and security tests should be in place early to make later migrations easier.
- Governance and compliance: In addition to security checks, data protection and regulatory requirements must always be observed.
- Software architecture: Internal requirements like frameworks and languages may only formally apply in production, but they should already be considered during Vibe Coding.
Only then can the benefits of Vibe Coding be realized without jeopardizing stability and security in live systems.
Conclusion
Vibe Coding is a useful accelerator for innovation in banking – as long as its limits are understood. It’s especially suited for rapid prototyping, idea validation, and collaboration between developers and business teams. It also has potential as a learning environment for new programming languages. But for live systems, the rule is clear: hands off. They require maintainable, scalable, and documented code that only traditional development processes can deliver. The key takeaway: use Vibe Coding consciously as a tool for experimentation and learning – while relying on classic processes for productive software development.
Want to read more about vibe coding and AI?







