 As the curtains draw on another transformative year, it’s time to reflect on the whirlwind of advancements and shifts that have sculpted 2023. In this comprehensive wrap-up, we at neosfer delve into the pivotal realms of Tech, Sustainability, Banking, and Venture Capital, unraveling the intricate tapestry of innovations and trends that have marked this year. From groundbreaking technological leaps to pivotal sustainability milestones, from the dynamic evolution of banking to a challenging venture capital landscape, we explore the key developments that have not only defined the year but are also set to shape the contours of our future
As the curtains draw on another transformative year, it’s time to reflect on the whirlwind of advancements and shifts that have sculpted 2023. In this comprehensive wrap-up, we at neosfer delve into the pivotal realms of Tech, Sustainability, Banking, and Venture Capital, unraveling the intricate tapestry of innovations and trends that have marked this year. From groundbreaking technological leaps to pivotal sustainability milestones, from the dynamic evolution of banking to a challenging venture capital landscape, we explore the key developments that have not only defined the year but are also set to shape the contours of our future
Year in Review: The 2023 Tech Revolution and the Rise of Sustainable Approaches to our Future
The Year in Tech
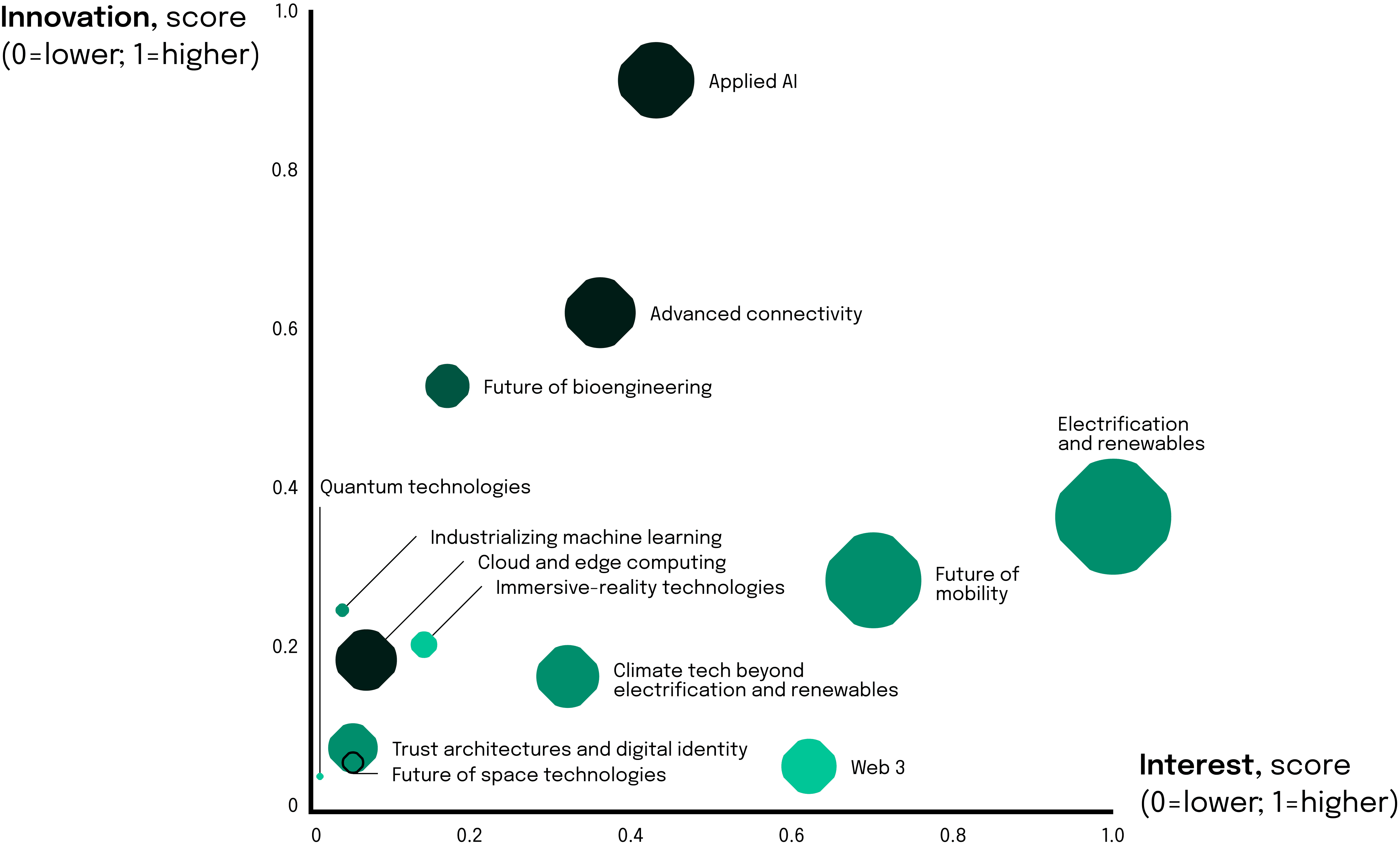
As we reflect on the tech landscape of 2023, our focus narrows on the most impactful areas. The visual representation underscores the high innovation and interest scores in Applied AI, Advanced Connectivity, Digital and Computing Innovations, and Sustainability in Tech. These domains have shown not only a high degree of innovation but also substantial engagement from the market, justifying their selection as our core topics.
Applied Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
In 2023, the realm of Applied AI and Machine Learning witnessed remarkable growth, profoundly impacting industries like healthcare, finance, retail, and logistics.
Retail businesses embraced AI for customer behavior analysis, offering a more customized shopping experience. Machine Learning, in particular, revolutionized inventory management and predictive analytics, enabling retailers to anticipate customer needs more accurately.
In 2023, the fusion of AI and renewable energy marked a significant leap towards eco-friendly power solutions. AI algorithms have become pivotal in enhancing the efficiency and reliability of renewable energy systems. They predict energy demand, optimize grid operations, and seamlessly integrate renewable sources, all while curbing greenhouse gas emissions.
One innovation to watch in this realm is the Global Renewables Watch. This live atlas harnesses AI and satellite imagery to map utility-scale solar and wind installations, offering a dynamic view of the clean energy transition and enabling the tracking of evolving trends. AI-driven models were pivotal in tracking environmental changes, aiding in the management of natural resources, and contributing to sustainable practices.
These advancements exemplified AI and ML’s growing significance, not just as tools for business optimization but also as catalysts for positive societal and environmental change.
Digital and Computing Innovations
Advancements in digital and computing innovations, particularly in cloud and edge computing, and quantum computing, marked a transformative year. Cloud computing, with its immense scalability, became a cornerstone in e-commerce and cybersecurity. It enabled vast data analytics capabilities and robust, secure cloud-based solutions, crucial for the growing needs of these sectors. Edge computing brought a paradigm shift, enhancing real-time data processing close to data sources, proving vital in manufacturing and in the burgeoning field of autonomous vehicles.
Quantum computing stepped into the limelight. Companies can leverage quantum computing for materials research, investigating binding characteristics and selectivity of metal organic frameworks that are used to filter carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere. Meanwhile, augmented and virtual reality technologies made leaps, significantly enhancing user experiences across various sectors. In education, they facilitated immersive learning experiences, while in healthcare, they enabled advanced patient treatment simulations. In the entertainment industry, these technologies offered more engaging and interactive experiences, changing the landscape of digital interaction.
These technologies collectively redefined digital infrastructure, promising more efficient, secure, and innovative computing solutions. This surge in digital and computing innovations signifies a move towards more integrated, intelligent, and user-centric technological environments.
Green Tech Innovations
In 2023, the tech industry embraced sustainability as a core innovation driver. Green computing initiatives, aimed at reducing environmental impact, became more prevalent. Efforts in this area included optimizing data center energy efficiency and developing eco-friendly hardware. Renewable energy technologies also saw significant advances, especially in solar and wind power, aligning tech operations with sustainability goals.
Innovations in battery technology and energy storage were pivotal in facilitating sustainable energy use, with tech giants investing heavily in carbon-neutral data centers. These advancements signaled a commitment to a sustainable future, integrating environmental considerations into every aspect of technology development and deployment.
The Future of Connectivity
In 2023, the advancements in connectivity, led by the proliferation of 5G technology, significantly impacted various sectors, marking a leap towards a more interconnected world. This enhanced connectivity facilitated sophisticated Internet of Things (IoT) implementations, transforming homes, industries, and public spaces into smart, efficient, and responsive environments. The emergence of smart cities became more pronounced, with improved data management and urban planning contributing to sustainable development and enhanced public services.
Payments, featuring in a majority of the basic services availed by citizens, form the core of every economic flow in a city, including salaries, consumer spending, business procurement. With smart finance, a citizen would only need one “global” card for the city to pay for groceries, take public transport, pay for other services or even apply for grants. These developments in connectivity technologies underpinned a transformative era, characterized by seamless interaction and increased efficiency, shaping the future of technology and its integration into daily life.
The Year 2023 in Sustainability
As we turn our eyes to sustainability in 2023, we witness a year that stands as a crucial juncture in our global environmental narrative. This segment of our annual wrap-up explores how the year has been pivotal in climate action and sustainable development. From record-breaking climatic events to significant strides in renewable energy, we delve into the transformative steps taken towards a more sustainable future, underscoring the urgent need for innovation and cooperation in this critical sphere.
A Pivot Point for Global Climate Action
The year 2023 stands as a stark reminder of the urgent challenges we face in terms of global environmental sustainability. According to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), 2023 shattered climate records, becoming the warmest year on record with average temperatures reaching approximately 1.40 degrees Celsius above the pre-industrial baseline. This rise in temperature was accompanied by a series of extreme weather events that caused widespread devastation and highlighted the fragility of our ecosystems.
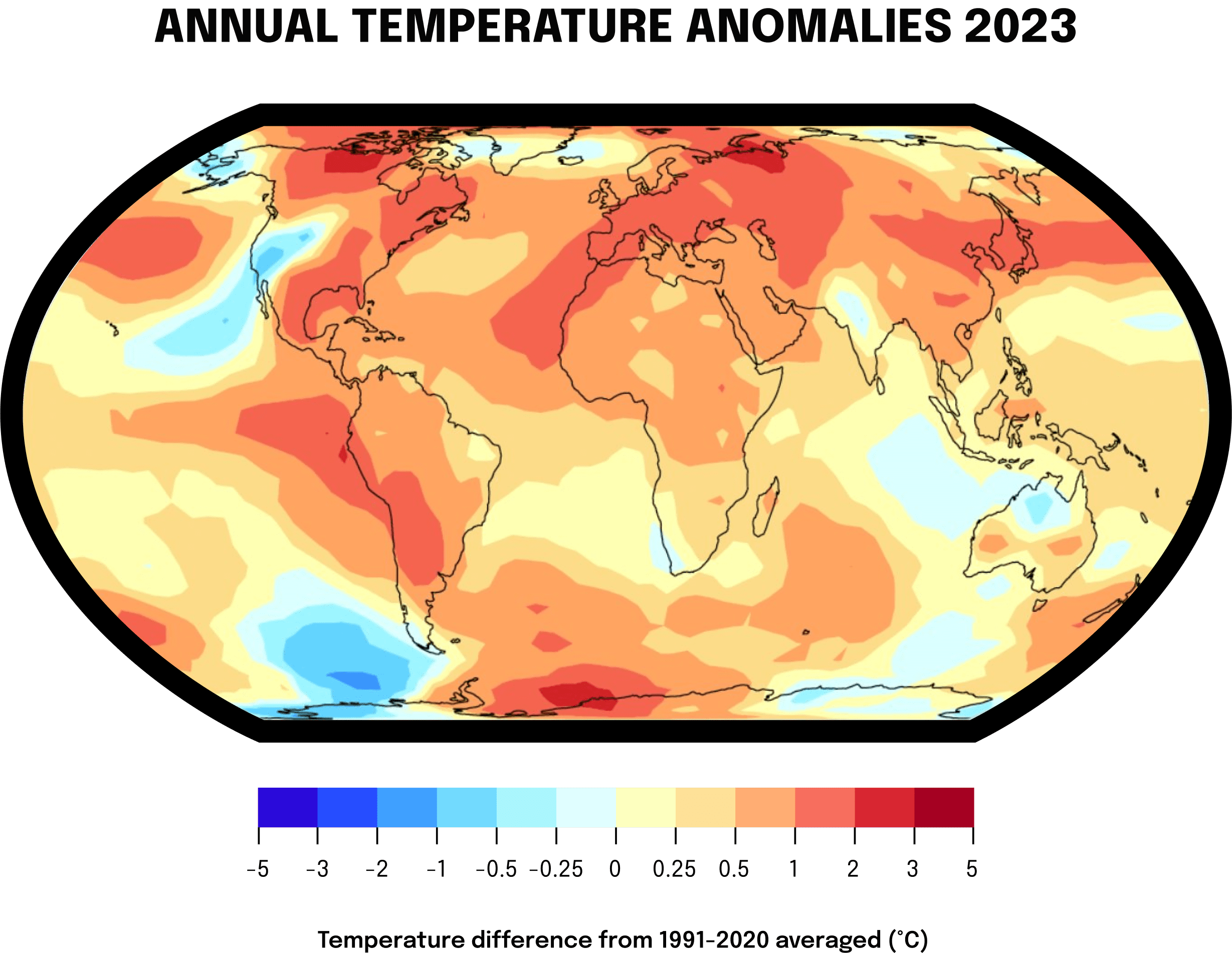
Greenhouse gas levels reached record highs, with carbon dioxide levels now 50% higher than in the pre-industrial era. This increase has contributed to a significant rise in global sea levels and a dramatic reduction in Antarctic sea ice, which hit its lowest extent on record, reducing by an area larger than France and Germany combined. These environmental changes have not only ecological ramifications but also profound socio-economic impacts, affecting food security and causing population displacements.
United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres emphasized the dire need for decisive climate action, urging world leaders to commit to limiting the global temperature rise to 1.5 degrees Celsius. He called for increased investment in renewable energy, which saw a growth of nearly 10% in 2022, predominantly from solar and wind sources. This push towards sustainable energy and the phasing out of fossil fuels is essential for mitigating the worst impacts of climate change.
The data and events of 2023 serve as a clarion call for immediate and concerted efforts to address the climate crisis. The environmental trends of the past year underscore the critical need for innovation, cooperation, and leadership in the pursuit of sustainability and climate resilience.
Sustainable Energy Developments: Progress in Sight
In 2023, the global energy sector showed a robust inclination towards sustainable energy developments, with investment in clean energy soaring by 25% since 2020, highlighting a decisive turn towards a green economy. The rapid adoption of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems. Solar PV generation increased by a record 270 TWh (up 26% from) in 2022, reaching almost 1 300 TWh, and this trend is set to continue in 2023. This surge in renewables, particularly solar energy, is propelled not just by the urgency to curb emissions but also by economic incentives and energy security considerations, especially for countries dependent on fuel imports. The clean energy sector’s investment pace has been brisk, with over USD 1 billion daily allocated to solar deployment and significant strides in manufacturing capacity for critical clean energy components like solar PV modules and EV batteries.
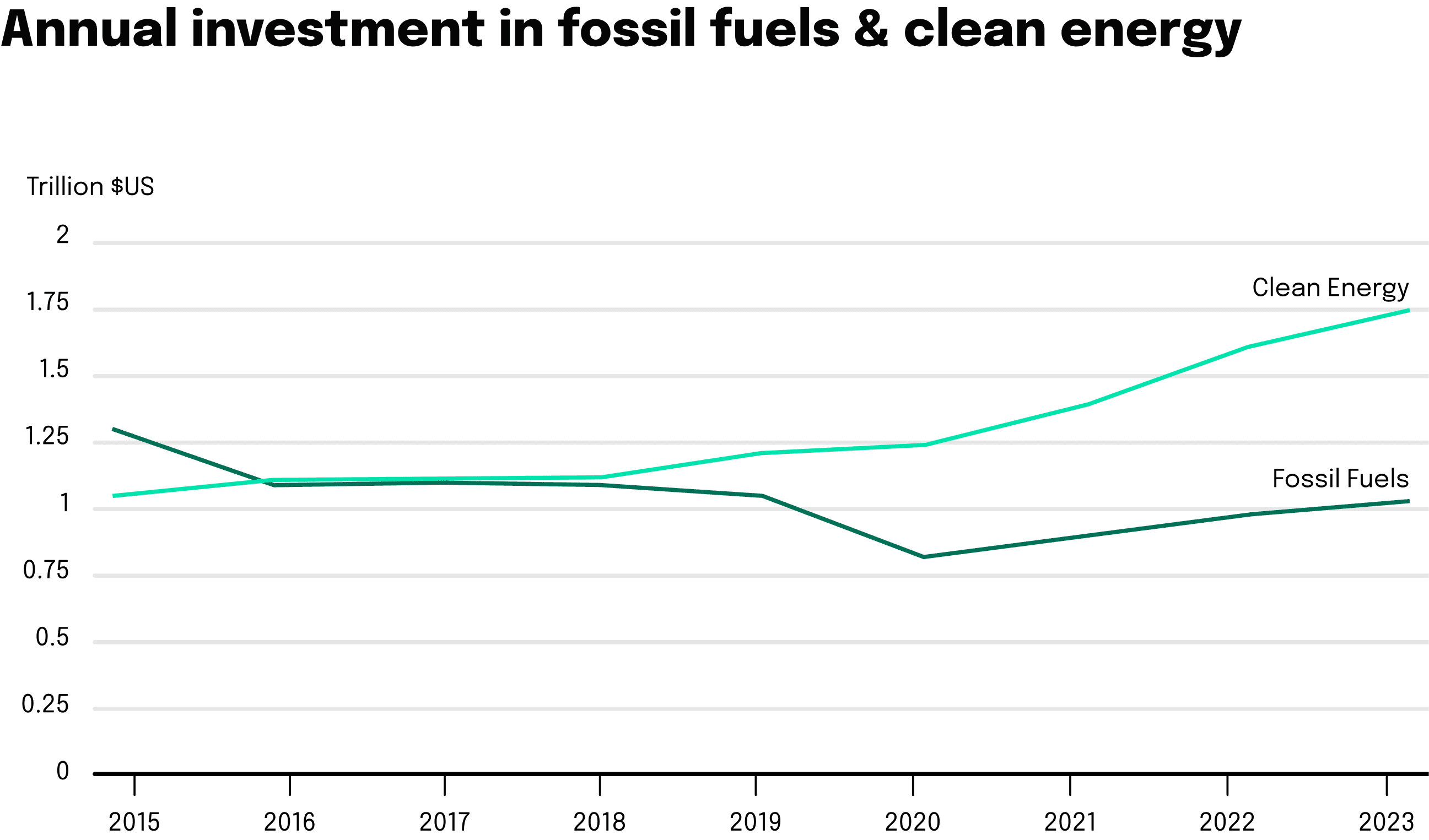
This year also witnessed a significant shift away from fossil fuels, with the rate of new fossil fuel assets being incorporated into the energy system slowing. Sales of vehicles with internal combustion engines plunged below pre-pandemic levels, and the introduction of coal- and natural gas-fired power plants halved from previous peaks. Furthermore, in many parts of Europe and the United States, heat pump sales have surpassed residential gas boiler sales with growth rates of over 11% globally, indicating a trend towards more sustainable home heating solutions.
Solar energy has been forecasted to account for more than half of the 80% new power capacity attributed to renewables by 2030. Despite these impressive figures, the potential for solar energy remains vastly untapped. With the current manufacturing plans, there’s potential for a manufacturing capacity of over 1200 GW of solar panels annually by the decade’s end, far surpassing the 500 GW projected for deployment in 2030. To realize this potential, enhancements in grid infrastructure and storage solutions are necessary to fully integrate solar energy into electricity systems. The global nature of the solar industry also highlights the importance of trade, especially given China’s significant production expansion, which far exceeds that of other countries, underscoring the need for a collaborative international approach to support solar deployment.
Regulatory Changes and Initiatives in 2023
The year 2023 marked a significant stride in the EU’s regulatory landscape towards bolstering sustainability efforts. In an ambitious move to become the world’s first climate-neutral continent, the EU fully adopted the “Fit for 55” legislation, setting forth a comprehensive plan to slash emissions by at least 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels, and paving the way for a cost-effective and equitable green transition.
The European Green Deal laid the groundwork for this transformational change, which not only promised to create new opportunities for innovation and investment but also aimed to enhance health and wellbeing across the continent. Every EU Member State committed to this historic push towards climate neutrality, underpinned by legally binding targets that spanned across all key sectors of the economy.
In transport, the EU introduced new CO2 standards mandating that all new cars and vans registered in Europe will be zero-emission by 2035, with interim reduction targets set for 2030. This decisive regulation aimed to establish a zero-emission mobility trajectory by mid-century. In addition, to support sustainable aviation and maritime transport, the minimum share of Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAF) required to be blended with kerosene increased, and carbon pricing was extended to the maritime sector to promote the uptake of renewable and low-carbon fuels.
The Green Deal Industrial Plan, introduced this year, sought to enhance the competitiveness of the EU’s net-zero industry and fast-track the climate neutrality transition. With an net-zero startup ecosystem valued at over €100 billion, the plan bolstered the EU’s role as a hub for industrial innovation and clean technology, setting an objective to fulfill at least 40% of the EU’s annual deployment needs for strategic net-zero technologies by 2030.
Moreover, the REPowerEU plan unveiled measures to accelerate renewable energy deployment, energy savings, and diversification of energy supplies. The EU legislated a new target for 2030 to increase its renewable capacity to a minimum of 42.5%, almost doubling the previous share of renewable energy within the EU. The directive entered into force in all EU countries on 20 November 2023.
The Year 2023 in Banking
In 2023, the landscape of digital banking witnessed a transformative evolution globally, driven by rapid technological advancements and changing consumer expectations. The integration of cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and cloud computing redefined banking services, offering customers enhanced convenience, security, and personalized experiences. With technological opportunities, associated risks didn’t become less significant. Therefore, let’s start with regulatory changes focused on the EU banking sector.
Regulatory Changes and Compliance: The European Banking Sector in a Year of Change
In 2023, the European banking sector faced a transformative regulatory landscape, characterized by stringent measures and compliance demands.
Capital Requirements and Stress Testing: The European Central Bank (ECB) and the European Banking Authority (EBA) tightened capital requirements under the Basel III framework. Banks in the EU were required to maintain a higher quality of capital, with the minimum Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratio being raised to 4.5%. Furthermore, the leverage ratio was increased to 3% for most banks, ensuring a stronger capital base to withstand financial shocks. The ECB also conducted rigorous stress tests, with approximately 70% of major banks passing the tests, indicating a robust banking system capable of enduring economic adversities.
Enhanced Transparency and Reporting: New reporting standards were introduced, requiring banks to disclose more detailed information on their risk exposures, lending practices, and investment portfolios. The Non-Performing Loan (NPL) ratio, a critical indicator of banks’ asset quality, saw an average reduction to 2.3% across the EU, compared to 3.5% in the previous year, reflecting improved credit risk management.
AML and KYC Compliance: Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations were significantly bolstered. The European Union’s AML authority increased its oversight, leading to a 25% rise in compliance spending by banks. This heightened focus resulted in a 40% increase in flagged suspicious transactions, demonstrating the efficacy of the new measures.
These regulatory changes in 2023 not only ensured a more stable and transparent banking environment in the EU but also signaled a shift towards more responsible and sustainable banking practices. The sector’s commitment to adapting to these regulations underlines its resilience and readiness to embrace a rapidly evolving financial landscape.
Digital Transformation in the European Banking Sector in 2023
In 2023, the European banking sector witnessed a significant push towards digital transformation, underpinned by a blend of innovation, strategic investment, and regulatory adaptation. This transformation was driven by the need to remain competitive and to meet the evolving demands of customers.
Nearly all significant European financial institutions have adopted digital transformation strategies, though the maturity levels and implementation varied. The primary objectives were enhancing customer experience and improving operational efficiency through automation and IT infrastructure modernization. However, a common challenge was developing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to monitor digital progress and assess the impact on profitability.
Investments and Resources: The financial commitment to digital transformation was notable, but still needs way more acceleration. Banks allocated on average 4% of their operational costs and 5.2% of their staff to these projects. This already is an increase and highlights the sector’s growing prioritization of digital initiatives, despite a prevalent challenge in accurately quantifying the cost and revenue impacts of these strategies. However, more initiatives from European banks are needed to be at the forefront of digital innovation and change.
Customer Digital Engagement: There was a significant shift towards digital customer engagement. On average, 46% of loans were concluded via digital channels, with 36% of customers using mobile banking and 21% using online banking. This change in customer behavior underscores the increasing reliance on digital platforms for banking services.
Technology Utilization: Almost all banks embraced cloud computing and application programming interfaces (APIs), with 60% utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) for various business applications. However, the use of distributed ledger technology (DLT) remained limited, with less than 20% of banks engaging in this area.
Sustainable and Ethical Banking in the EU in 2023
In 2023, the European banking sector’s approach to sustainability and ethical banking underwent significant developments, underpinned by regulatory changes, increased emphasis on environmental disclosures, and a growing consumer demand for green banking alternatives.
The European Banking Authority (EBA) introduced mandatory climate disclosures for banks starting from December 2023. This move was aimed at pushing banks to gather necessary information to manage climate risks effectively. The disclosures require banks to reveal their exposure to transition risk, such as carbon-intensive activities and financed emissions, and physical risk from climate change impacts. The EBA’s guidelines were part of broader efforts to incorporate sustainability considerations into banking operations and supervision.
There was a 27% increase in banks’ environmental disclosures between 2014 and 2020, reflecting a growing focus on climate topics. However, research found discrepancies between banks’ environmental disclosures and their lending practices. Notably, banks with high environmental disclosures tended to extend more credit to “brown industries,” raising concerns about the alignment of sustainability commitments with actual lending practices.
Sustainable fintech companies and neo-banks witnessed significant growth, with reported yearly growth rates of around 10%. This growth highlighted the increasing consumer demand for ethical and environmentally-conscious banking services. However, sustainable banks were still underrepresented in key EU financial decision-making bodies, indicating a need for greater inclusion and representation of these institutions in shaping the EU’s sustainable finance agenda. ESG banks in the EU have shown robust performance over the past decade, with returns on assets and equity doubling compared to their conventional peers. Their involvement in policy-making processes is crucial for driving positive social and environmental change within the banking sector.
Venture Capital in 2023
In 2023, the venture capital (VC) landscape, particularly in the area of strategic investments in emerging technologies, experienced notable trends and shifts. Key developments in various sectors and the overall funding scenario provided a comprehensive picture of the VC environment for the year.
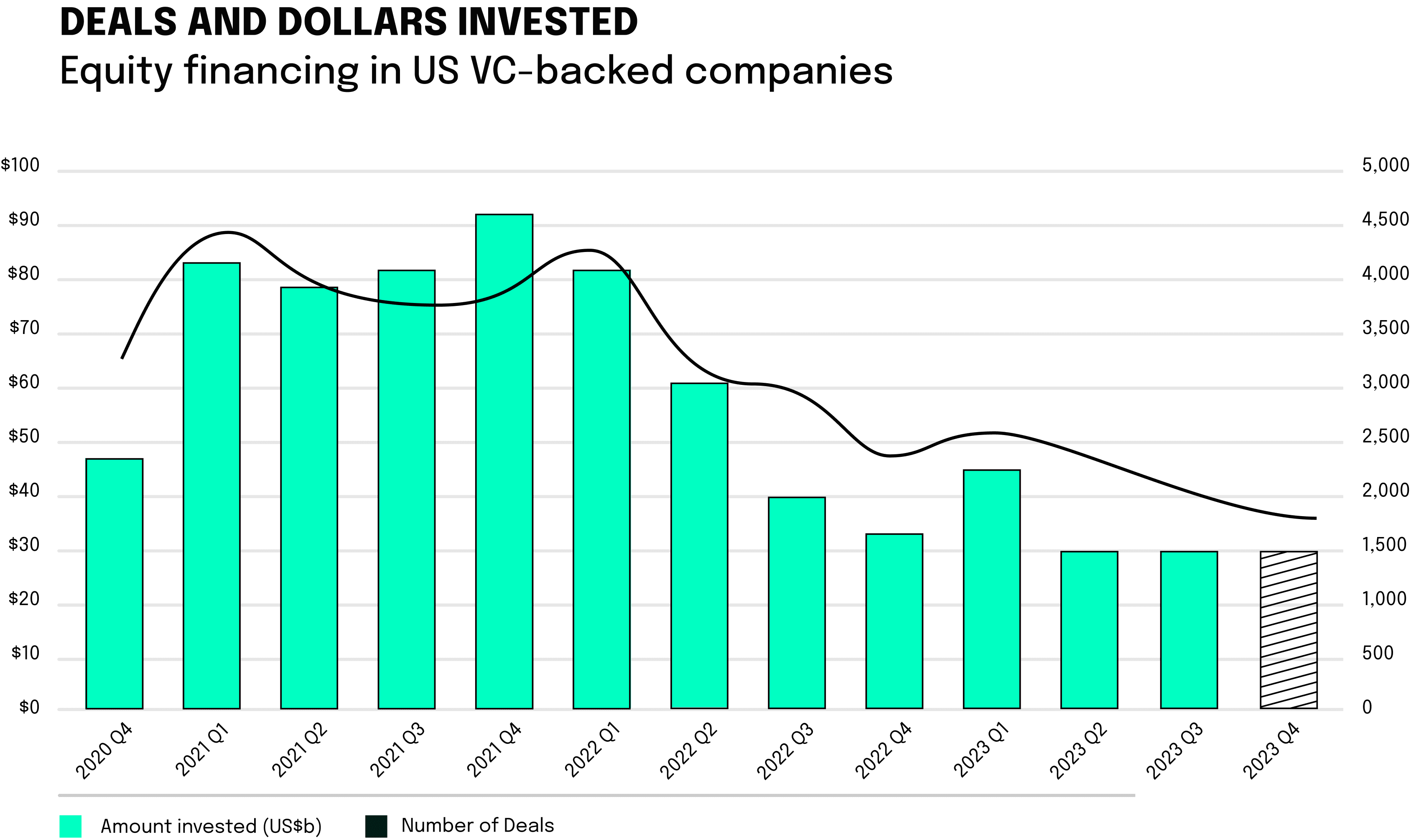
Global venture capital investment dropped for the sixth consecutive quarter in Q2’2023 – falling from $86.2 billion across 10,121 deals in Q1’23 to $77.4 billion across 7,783 deals in Q2’23. Increasing interest rates, stubbornly high inflation, domestic and geopolitical challenges -including the protracted war in Ukraine, and ongoing concerns about the stability of the global banking system all combined to make it a challenging quarter for VC investment across regions, despite global interest in Generative AI. Despite this, there was a significant amount of early-stage activity, with half of the VC deals in Q2 2023 being seed and Series A, amounting to $7.2 billion. By Q3 2023, the total VC investment maintained a flat trend from the previous quarter, being at $77 billion. Q4 did not bring any significant positive changes and will most likely show a flat curve. Marking the end to a challenging year for the deployment of capital and for startups alike.
These global VC developments can be visualized particularly well in the U.S. VC market, which can be seen here as a proxy for other Western VC markets. The sharp decline in deals and invested sums since the start of 2022 is particularly clear here.
Hot Areas and Global Developments in 2023
Throughout the year, several sectors attracted significant VC investments:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI continued to be a dominant field, attracting substantial investments due to its transformative potential across various industries, including healthcare, finance, cybersecurity, and autonomous systems.
- Sustainability and Clean Tech: The clean tech sector saw increased investment, driven by a global emphasis on sustainability. This sector includes startups focusing on environmentally friendly solutions, renewable energy, waste management, and efficient resource utilization.
- Health Tech and Digital Health Solutions: The digital transformation in healthcare, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, led to significant investments in health tech, including telemedicine platforms, remote patient monitoring, and health data analytics.
The number of active Corporate VCs globally has increased. In 2023, the number of CVC funds surveyed rose to 209, up from 164 the previous year, showcasing a growing interest in corporate venture investments. This expansion highlights the strategic importance of CVCs in acting as sensors for their parent companies, especially in sectors like technology, where they play a crucial role in identifying and capitalizing on emerging trends.
In Europe, there were five clear sectors in which VCs invested the most (these numbers are estimations based on the first three quarters of 2023):
- Software (including SaaS, FinTech, and e-commerce): $36.5 billion
- Healthcare: $16.4 billion
- Consumer: $11.1 billion
- Industrials: $6.2 billion
- Energy: $4.4 billion
Sustainable and Impact Investing in 2023
In 2023, the investment landscape witnessed a notable surge in the pursuit of sustainable and impact investments. This shift reflects a growing awareness among investors of the interconnectedness between financial returns and environmental and social responsibility.
Impact and Markets’ Impact Investing Global Market Report 2023 found that the global impact investing market grew from $420.91 billion in 2022 to $495.82 billion in 2023 at a compound annual growth rate of 17.8%. VCs also showed a marked interest in startups that align with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). A study by PitchBook and the ImpactAssets Foundation found that in 2023, 60% of venture capitalists considered SDG alignment a critical factor in their investment decisions. Especially the clean tech sector, which includes startups dedicated to developing environmentally friendly solutions, renewable energy, waste management, and efficient resource utilization, attracted notable venture capital investment.
Impact startups, particularly those in the climate action and affordable and clean energy sectors, have collectively raised significant funding since 2017. These sectors attract the majority of impact investment, indicating a strong investor interest in climate-related initiatives. However, it’s also observed that startups addressing people-related SDGs, such as Life Below Water and Decent Work and Economic Growth, are among the most underfunded yet fastest growing. We can view this a negative side, however, for VCs this offers great investments and ROI opportunities in the future. A study by the Cambridge Institute for Sustainability Leadership found that impact investments outperformed traditional investments by 1.4% annually between 2012 and 2021.
Your Executive Summary for 2023 in Tech, Sustainability, Banking and VC
The year 2023 has been a period of significant advancement and transformation across various sectors, prominently in Technology, Sustainability, Banking, and Venture Capital. This summary encapsulates the key developments and trends observed in each of these areas.
Technology in 2023: The tech sector saw remarkable innovations, particularly in Applied AI, Advanced Connectivity, Digital and Computing Innovations, and Sustainability. AI and Machine Learning greatly impacted healthcare, finance, retail, and logistics, enhancing operations and contributing to sustainability. Digital and computing innovations, including cloud and edge computing, quantum computing, and AR/VR technologies, redefined user experiences and the digital infrastructure. Green tech innovations focused on reducing environmental impact and advancing renewable energy technologies.
Sustainability in 2023: The year marked a critical point for global climate action. Record high temperatures and extreme weather events underscored the urgency of addressing climate challenges. The energy sector witnessed a shift towards sustainable energy, with significant investments in solar and wind power and advancements in battery technology. Regulatory initiatives, particularly in the EU, aimed at reducing emissions and promoting sustainability, played a crucial role in shaping the sustainability landscape.
Banking in 2023: The banking sector experienced a transformative year with advancements in digital banking driven by AI, blockchain, and cloud computing. Regulatory changes in the EU banking sector, including stricter capital requirements and enhanced transparency, aimed at creating a more stable and transparent banking environment. The European banking sector’s approach to sustainability also evolved, with increased emphasis on environmental disclosures and ethical banking practices.
Venture Capital in 2023: The VC landscape was marked by significant investments in emerging technologies, despite fluctuations in total investment throughout the year. Key areas of investment included AI, sustainability, clean tech, health tech, and digital health solutions. Geographically, notable growth in VC investments was observed in the UK, China, and the US, despite economic challenges. Corporate Venture Capital (CVC) also saw an increase in active funds, highlighting their strategic importance in technology investment.
Sustainable and Impact Investing in 2023: There was a marked increase in sustainable and impact investments, with a focus on startups aligning with the UN SDGs. Despite a general downturn in impact startup funding, sectors like clean tech attracted significant investments. Notable funding rounds in sustainability-focused companies underscored the growing importance of environmentally friendly solutions.
This year has seen everything from challenging global economic conditions, critical periods for climate change, as well as a lot of technical innovations and changes for the consumer. Also the banking and VC sector were heavily impacted by either regulatory or environmental factors, marking the beginning to an eventful year 2024.

